Trichomes
Hair-like structures that make cannabis plants look frosty are called
trichomes. They are most densely located on the flowers, but they cover the whole aerial part of the plant. There are two primary types of trichomes:
glandular (with a gland) and
non-glandular (without a gland).
1
Non-glandular trichomes are only comprised of stalks. They do not produce
cannabinoids or
terpenes (Figure 1).
1
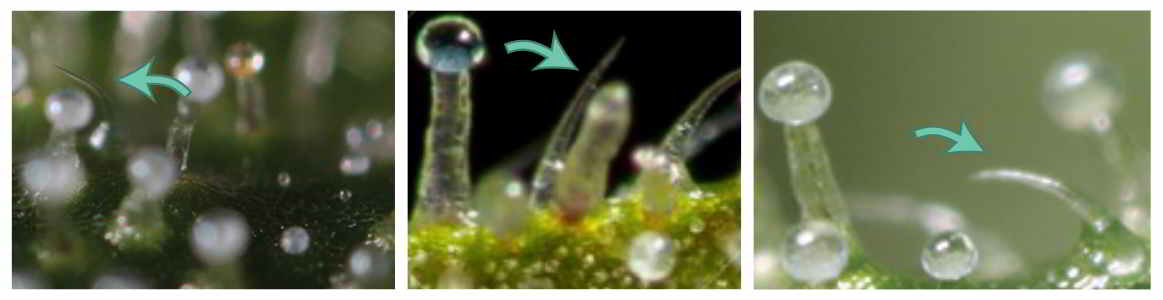 Figure 1: A photo of a female cannabis plant with clearly visible different types of trichomes. Non-glandular trichomes are indicated with green arrows.
Glandular trichomes
Figure 1: A photo of a female cannabis plant with clearly visible different types of trichomes. Non-glandular trichomes are indicated with green arrows.
Glandular trichomes comprise a head-shaped gland where cannabinoid and terpenoid synthesis takes place. In most of them, the gland sits on top of a visible stalk, while the rest only comprise the gland with a very short stalk. There are 3 primary types of glandular trichomes on female plants: 1)
capitate-stalked, 2)
capitate-sessile, and 3)
bulbous.
2
Glandular trichomes
Capitate-stalked trichomes
They are the largest (100+ µm) and can be easily seen with the naked eye.
2 They have a stalk and a big head where most of the cannabinoids and terpenes are located. For the most part, these trichomes are responsible for the frosty appearance of cannabis flowers.
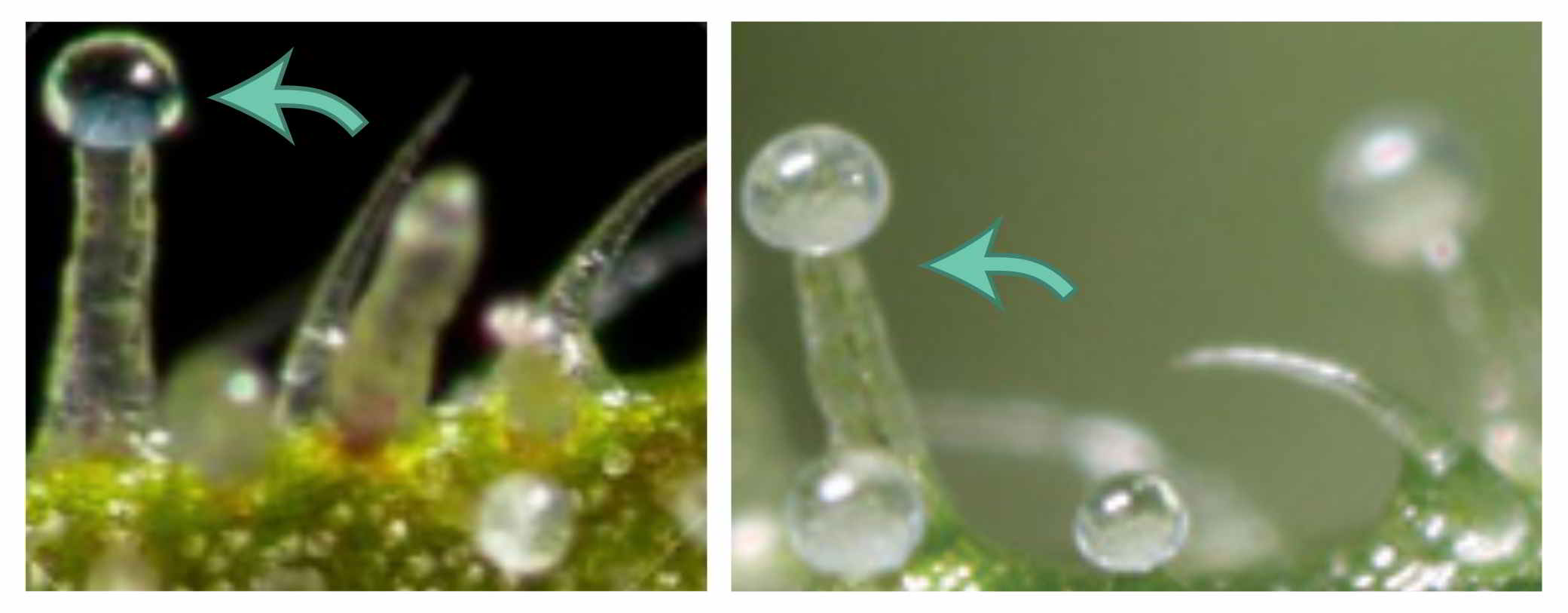 Figure 2: Capitate-stalked trichomes with a gland sitting on a stalk, marked with green arrows.
Capitate-sessile trichomes
Figure 2: Capitate-stalked trichomes with a gland sitting on a stalk, marked with green arrows.
Capitate-sessile trichomes
With the size ranging between 25 µm and 100 µm, capitate-sessile trichomes are smaller than the capitate-stalked ones (Figure 3). On young plants these trichomes appear as if they do not have a stalk, hence the name “sessile” {call-out, text: As per definitions from Oxford Languages: (of a plant or animal structure) attached directly by its base without a stalk or peduncle.} They produce cannabinoids and terpenes in their glands.
1
 Figure 3: Capitate-sessile trichomes with visible glands appearing without stalks.
Bulbous trichomes
Figure 3: Capitate-sessile trichomes with visible glands appearing without stalks.
Bulbous trichomes
The smallest trichomes on cannabis plants (10-25 µm), they are spread throughout the surface of the entire plant.
2 These trichomes are less abundant and slightly smaller than the capitate-sessile ones. They are made up of a stalk and a gland, just like capitate-stalked trichomes, but are physically much smaller in comparison (Figure 4). Their role is still unknown and it is not yet proven whether they produce cannabinoids and terpenes.
2
 Figure 4: Capitate-sessile trichomes are barely visible next to other trichomes.
Figure 4: Capitate-sessile trichomes are barely visible next to other trichomes.- Upton, Roy; Craker, Lyle; ElSohly, Mahmoud; Romm, Aviva; Russo, Ethan; Sexton, Michelle (2014). Cannabis Inflorescence Standards of identify, analysis and quality control (65). American Herbal Pharmacopoeia.
- Pertwee, Roger G. (2014). Handbook of Cannabis. Handbooks in Psychopharmacology, 44(8), 085201.
 Figure 1: A photo of a female cannabis plant with clearly visible different types of trichomes. Non-glandular trichomes are indicated with green arrows.
Glandular trichomes comprise a head-shaped gland where cannabinoid and terpenoid synthesis takes place. In most of them, the gland sits on top of a visible stalk, while the rest only comprise the gland with a very short stalk. There are 3 primary types of glandular trichomes on female plants: 1) capitate-stalked, 2) capitate-sessile, and 3) bulbous.2
Figure 1: A photo of a female cannabis plant with clearly visible different types of trichomes. Non-glandular trichomes are indicated with green arrows.
Glandular trichomes comprise a head-shaped gland where cannabinoid and terpenoid synthesis takes place. In most of them, the gland sits on top of a visible stalk, while the rest only comprise the gland with a very short stalk. There are 3 primary types of glandular trichomes on female plants: 1) capitate-stalked, 2) capitate-sessile, and 3) bulbous.2
 Figure 2: Capitate-stalked trichomes with a gland sitting on a stalk, marked with green arrows.
Capitate-sessile trichomes
With the size ranging between 25 µm and 100 µm, capitate-sessile trichomes are smaller than the capitate-stalked ones (Figure 3). On young plants these trichomes appear as if they do not have a stalk, hence the name “sessile” {call-out, text: As per definitions from Oxford Languages: (of a plant or animal structure) attached directly by its base without a stalk or peduncle.} They produce cannabinoids and terpenes in their glands.1
Figure 2: Capitate-stalked trichomes with a gland sitting on a stalk, marked with green arrows.
Capitate-sessile trichomes
With the size ranging between 25 µm and 100 µm, capitate-sessile trichomes are smaller than the capitate-stalked ones (Figure 3). On young plants these trichomes appear as if they do not have a stalk, hence the name “sessile” {call-out, text: As per definitions from Oxford Languages: (of a plant or animal structure) attached directly by its base without a stalk or peduncle.} They produce cannabinoids and terpenes in their glands.1
 Figure 3: Capitate-sessile trichomes with visible glands appearing without stalks.
Bulbous trichomes
The smallest trichomes on cannabis plants (10-25 µm), they are spread throughout the surface of the entire plant.2 These trichomes are less abundant and slightly smaller than the capitate-sessile ones. They are made up of a stalk and a gland, just like capitate-stalked trichomes, but are physically much smaller in comparison (Figure 4). Their role is still unknown and it is not yet proven whether they produce cannabinoids and terpenes.2
Figure 3: Capitate-sessile trichomes with visible glands appearing without stalks.
Bulbous trichomes
The smallest trichomes on cannabis plants (10-25 µm), they are spread throughout the surface of the entire plant.2 These trichomes are less abundant and slightly smaller than the capitate-sessile ones. They are made up of a stalk and a gland, just like capitate-stalked trichomes, but are physically much smaller in comparison (Figure 4). Their role is still unknown and it is not yet proven whether they produce cannabinoids and terpenes.2
 Figure 4: Capitate-sessile trichomes are barely visible next to other trichomes.References:
Figure 4: Capitate-sessile trichomes are barely visible next to other trichomes.References:_logo.svg)