What are cannabinoids?
Cannabinoids are a specific type of fatty compounds that mostly plants, but also our bodies, can synthesize. Apart from natural synthesis, scientists managed to synthesize them chemically. Therefore, there are three different types of cannabinoids:
[1]
phytocannabinoids – made by plants,
[2] endogenous cannabinoids, or
endocannabinoids – made by our bodies,
[3]
synthetic cannabinoids – chemically synthesized for drug development and research.
Regardless of the origin, these compounds can bind to cannabinoid receptors, i.e. the binding places in our body that make up the
endocannabinoid system.
Plant-derived compounds are known as
phytocannabinoids.
1, 2 These compounds are mainly found in the cannabis plant, although some of them can also be found in other plants. Up to 2016, researchers identified 113 of them in cannabis plants.
3
Our bodies also makes these compounds and we call them
endocannabinoids.
4 The two of them which scientists studied the most are
anandamide (AEA)5 and
2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG).
6
An example of
synthetic cannabinoids is nabilone, a registered medicine with synthetic THC.
7
The two main cannabis compounds are
THC (Δ
9-tetrahydrocannabinol) and
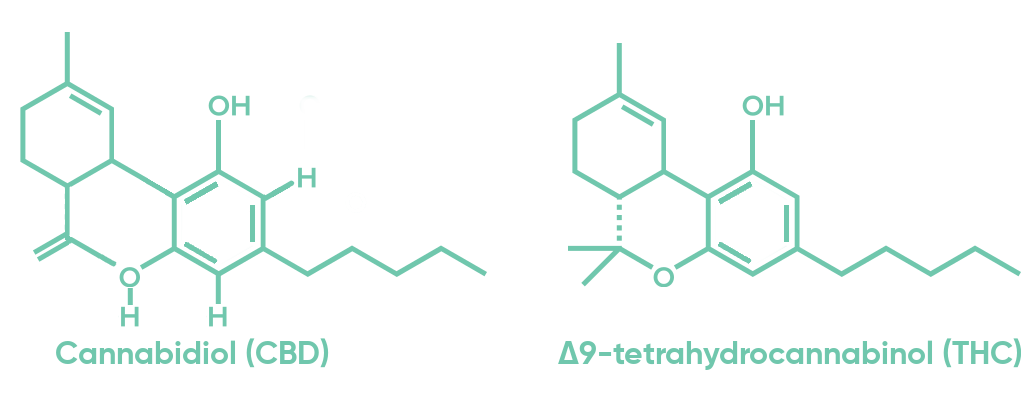
CBD (cannabidiol). THC is the main psychoactive compound in cannabis.
8 CBD is not psychoactive in the same way and may counteract some of the side effects of THC.
9 Studies have also shown that CBD can help with anxiety and epilepsy.
10, 11, 12 Other notable compounds identified in cannabis are: cannabichromene (CBC), cannabigerol (CBG), cannabinol (CBN), tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV). Researchers have yet to thoroughly study most of these compounds and their effects on humans.
- Russo, Ethan B. (2016). Beyond Cannabis: Plants and the Endocannabinoid System. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 37(7), 594--606.
- Woelkart, Karin; Salo-Ahen, Outi M. H.; Bauer, Rudolf (2008). CB receptor ligands from plants. Current topics in medicinal chemistry, 8(3), 173--186.
- Aizpurua-Olaizola, Oier; Soydaner, Umut; Ozturk, Ekin; Schibano, Daniele; Simsir, Yilmaz; Navarro, Patricia; Etxebarria, Nestor; Usobiaga, Aresatz (2016). Evolution of the Cannabinoid and Terpene Content during the Growth of Cannabis sativa Plants from Different Chemotypes. Journal of natural products, 79(2), 324--331.
- Pertwee, Roger G. (2015). Endocannabinoids and Their Pharmacological Actions. Handbook of experimental pharmacology (1--37).
- Devane, W. A.; Hanus, L.; Breuer, A.; Pertwee, R. G.; Stevenson, L. A.; Griffin, G.; Gibson, D.; Mandelbaum, A.; Etinger, A.; Mechoulam, R. (1992). Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science (New York, N.Y.), 258(5090), 1946--1949.
- Mechoulam, R.; Ben-Shabat, S.; Hanus, L.; Ligumsky, M.; Kaminski, N. E.; Schatz, A. R.; Gopher, A.; Almog, S.; Martin, B. R.; Compton, D. R. (1995). Identification of an endogenous 2-monoglyceride, present in canine gut, that binds to cannabinoid receptors. Biochemical pharmacology, 50(1), 83--90.
- Wissel, Jörg; Haydn, Tanja; Müller, Jörg; Brenneis, Christian; Berger, Thomas; Poewe, Werner; Schelosky, Ludwig D. (2006). Low dose treatment with the synthetic cannabinoid Nabilone significantly reduces spasticity-related pain. Journal of Neurology, 253(10), 1337--1341.
- Borgelt, Laura M.; Franson, Kari L.; Nussbaum, Abraham M.; Wang, George S. (2013). The pharmacologic and clinical effects of medical cannabis. Pharmacotherapy, 33(2), 195--209.
- Iseger, Tabitha A.; Bossong, Matthijs G. (2015). A systematic review of the antipsychotic properties of cannabidiol in humans. Schizophrenia Research, 162(1-3), 153--161.
- Bergamaschi, M. M.; Queiroz, R. H. C.; Chagas, M. H. N.; de Oliveira, D. C. G.; De Martinis, B. S.; Kapczinski, F.; Quevedo, J.; Roesler, R.; Schröder, N.; Nardi, Antonio E.; Martín-Santos, R.; Hallak, J. E. C.; Zuardi, A. W.; Crippa, J. A. S. (2011). Cannabidiol reduces the anxiety induced by simulated public speaking in treatment-naïve social phobia patients. Neuropsychopharmacology, 36(6), 1219--26.
- Devinsky, Orrin; Cross, J. Helen; Laux, Linda; Marsh, Eric; Miller, Ian; Nabbout, Rima; Scheffer, Ingrid E.; Thiele, Elizabeth A.; Wright, Stephen (2017). Trial of Cannabidiol for Drug-Resistant Seizures in the Dravet Syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine, 376(21), 2011--2020.
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (2017). The Health Effects of Cannabis and Cannabinoids. Nap 24625 (440). National Academies Press.
 Cannabinoids are a specific type of fatty compounds that mostly plants, but also our bodies, can synthesize. Apart from natural synthesis, scientists managed to synthesize them chemically. Therefore, there are three different types of cannabinoids:
[1] phytocannabinoids – made by plants,
[2] endogenous cannabinoids, or endocannabinoids – made by our bodies,
[3] synthetic cannabinoids – chemically synthesized for drug development and research.
Regardless of the origin, these compounds can bind to cannabinoid receptors, i.e. the binding places in our body that make up the endocannabinoid system.
Plant-derived compounds are known as phytocannabinoids.1, 2 These compounds are mainly found in the cannabis plant, although some of them can also be found in other plants. Up to 2016, researchers identified 113 of them in cannabis plants.3
Our bodies also makes these compounds and we call them endocannabinoids.4 The two of them which scientists studied the most are anandamide (AEA)5 and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG).6
An example of synthetic cannabinoids is nabilone, a registered medicine with synthetic THC.7
The two main cannabis compounds are THC (Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol). THC is the main psychoactive compound in cannabis.8 CBD is not psychoactive in the same way and may counteract some of the side effects of THC.9 Studies have also shown that CBD can help with anxiety and epilepsy.10, 11, 12 Other notable compounds identified in cannabis are: cannabichromene (CBC), cannabigerol (CBG), cannabinol (CBN), tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV). Researchers have yet to thoroughly study most of these compounds and their effects on humans.
References:
Cannabinoids are a specific type of fatty compounds that mostly plants, but also our bodies, can synthesize. Apart from natural synthesis, scientists managed to synthesize them chemically. Therefore, there are three different types of cannabinoids:
[1] phytocannabinoids – made by plants,
[2] endogenous cannabinoids, or endocannabinoids – made by our bodies,
[3] synthetic cannabinoids – chemically synthesized for drug development and research.
Regardless of the origin, these compounds can bind to cannabinoid receptors, i.e. the binding places in our body that make up the endocannabinoid system.
Plant-derived compounds are known as phytocannabinoids.1, 2 These compounds are mainly found in the cannabis plant, although some of them can also be found in other plants. Up to 2016, researchers identified 113 of them in cannabis plants.3
Our bodies also makes these compounds and we call them endocannabinoids.4 The two of them which scientists studied the most are anandamide (AEA)5 and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG).6
An example of synthetic cannabinoids is nabilone, a registered medicine with synthetic THC.7
The two main cannabis compounds are THC (Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol). THC is the main psychoactive compound in cannabis.8 CBD is not psychoactive in the same way and may counteract some of the side effects of THC.9 Studies have also shown that CBD can help with anxiety and epilepsy.10, 11, 12 Other notable compounds identified in cannabis are: cannabichromene (CBC), cannabigerol (CBG), cannabinol (CBN), tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV). Researchers have yet to thoroughly study most of these compounds and their effects on humans.
References:_logo.svg)